Hypospadias is a usual birth defect of the penis in which the urethra (the tube which carries urine from the bladder to outside) is not at the tip of the penis. It may be situated anywhere on the undersurface of the penis to the scrotum.
A condition called chordee is was seen along with hypospadias. Chordee is an unusual downward curve of the penis. This may occurs with or without a hypospadias. Categorization of hypospadias was done based on the position of the urethral opening.
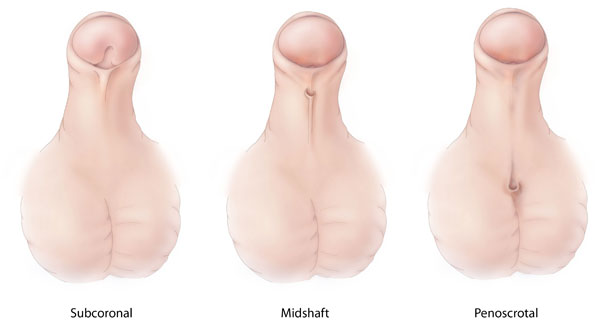
The types of hypospadias may include:
-
Distal or glanular: Most familiar form when opening is found near the penis head.
-
Midshaft: when opening was found in the center to the lower shaft of the penis.
-
Penoscrotal: when opening was on the scrotum.
-
Perineal: when opening was behind the scrotal sac. These are the most extreme forms of hypospadias.
SYMPTOMS:
Usually, hypospadias is noticed at the time of birth. Along with the misplaced or absent opening, the foreskin is usually incomplete and forms a hood. This is known as dorsal hood. Yet, some newborn boys have irregular foreskin with a usual positioned urethral opening. If a hypospadias or chordee malformation is not repaired, child may comprise these issues when he grows: His urine stream may be hard to direct and difficult to control, the penis may be curve as he grows causes sexual dysfunction in his later stages of his life, if the urethral opening is behind or near to the scrotum, he may suffers with fertility problems later in his life.
CAUSES:
The main cause of hypospadias is unknown. Most common, it is the only unusual finding, even though at about 10% of cases of hypospadias can be part of a disorder with multiple abnormalities. Genetics, the environment and hormones may be main factors that may influence the improvement of this defect.
DIAGNOSIS:
Hypospadias is generally diagnosed in the newborn babies by the typical appearance of the penis. The urinary opening (“meatus”) is lower than regular, and most of the boys have only incomplete development of the foreskin, lacking the regular covering for the glans on the bottom. The abnormal “hooded” foreskin calls notice to the condition. The treatment generally suggested for hypospadias surgery.

