Kidney Transplantation is the medical procedure in which placing a fully functioning kidney into a person with severe kidney failure. This procedure is usually an elective one, performed in patients who have undergone careful preoperative assessment and preparation, where dialysis enables these patients to be maintain in comparatively good condition till the time of surgery. The transplanted kidney may begin from a deceased donor (cadaver transplantation) or from a unrelated or related person (living transplantation). 50% of all kidney transplants are expected from cadaver donors. Normal functional levels of cadaveric donations stretch that interval to 7–15 days. Hospital stay is typically for 4–7 days.
PROCEDURE:
-
A cadaveric kidney comes from a deceased donor.
-
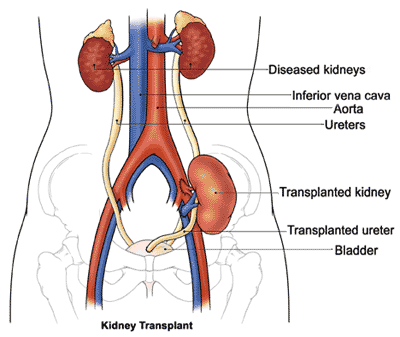
This surgery main motto is to supply a single, fully functioning kidney. One kidney provides more than sufficient filtration and regulating capacity for all the purpose and is graft into its own location while the existing (non-functioning) kidneys remain in place.
-
The existing kidneys are removed only if they cause persistent infection or high blood pressure, and they will not interfere with the transplant procedure or functioning of the new organ.
-
As soon as the transplanted kidney is linked to the blood vessels, it will starts purifying the blood of waste products.
-
Patients are required to take medications that suppress the immune system for the rest of their lives to avoid the rejection of the kidney grafts.
A cadaver kidney transplant occasionally will be temporarily slow in the function, this condition was called as acute tubular necrosis (ATN) or “sleepy” kidney. Patient need to undergo dialysis a few times. A “sleepy” kidney usually starts working in two to four weeks.
After kidney transplant surgery, the mainstays of drug therapy are generally a combination of 2 to 3 immunosuppressive medications, such as prednisone, cyclosporine, tacrolimus, or rapamycin, and sometimes azathioprine or cellcept. Initially, higher doses of these drugs are used as the risk of rejection is highest immediately after transplantation.

